Your definition of a metaverse likely differs from Facebook, but they don’t care. Have a look at the VR remote workplace now in open beta.
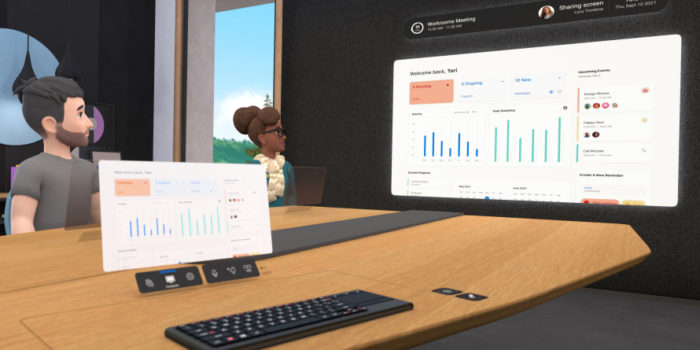

Your definition of a metaverse likely differs from Facebook, but they don’t care. Have a look at the VR remote workplace now in open beta.
It’s August 16th. Donations made here for earthquake relief efforts in Haiti are being shared by 17 organizations including Doctors Without Borders and World Central Kitchen.
Today’s Spotlight is 1,046 words — about a 4 minute read.
Quoted: “That’s not a slippery slope; that’s a fully built system just waiting for external pressure to make the slightest change.” — Electronic Frontier Foundation statement regarding Apple’s announcement about about a new plan to scan iPhones and other devices it makes. Scroll down to read more about this week’s “Spotlight Explainer” topic.
a) As politicians and pundits debate vaccine passports, the market has spoken. Etsy sellers are doing well with homemade vaccine cardholders. One leather shop sold 10,000 in three months. (Morning Brew)
b) Industry consolidation continues throughout digital marketing with Newfold Digital’s acquisition of search engine optimization software maker Yoast. Newfold already owns Network Solutions, Register.com and other big names.
Separately, NortonLifeLock and virus software maker Avast merged in an $8.1 billion dollar deal. NLL announced last December that they had purchased virus software company Avira.
Still more acquisition news: Fearing regulatory approval problems, DoorDash ended talks to acquire Instacart, according to an exclusive in The Information.
c) Zoom announced “Focus Mode,” a webinar-like setting that allows teachers to see all students, but students to only see their teacher. The Verge has coverage.
Google has provided website owners with a workflow to “evaluate website health and identify pain points, debug, and continuously monitor performance.” The comprehensive tool allows organizations to consider the new user experience optimization that Google is mandating, err, recommending, for sites.
These are part of the secret algorithms that Google uses to rank pages for different queries. In typical Google fashion, you’ll need a developer and a search marketer to get through the workflow. There are specialists in either discipline who understand enough of the other side to muddle through, but this is a highly technical overview complete with report templates and guides.
If that person in your organization isn’t you, send them this brand-new process that Google published last week.
Apple’s foray as Privacy Champion lasted as long as it took them to fling regulatory mud on Facebook before announcing that iOS 15 will automatically scan iPhone, Mac, and iPad devices looking for child pornography images.
Yes, society needs to do more to stop people from viewing or collecting child pornography.
No, Apple is not the organization that should be doing this and certainly not this way.
What Apple’s announcement says: “Instead of scanning images in the cloud, the system performs on-device matching using a database of known CSAM (Child Sexual Abuse Material) image hashes provided by … child safety organizations.” Read the whole announcement here.
What critics say: The technology can be used to scan any image on a user’s phone. And Apple devices are used around the world, including places where authoritarian governments can easily co-opt Apple or the technology for surveillance or other nefarious purposes.
Other complaints: How long before other device makers do this and providers prohibit companies that don’t? And when and where does the category get expanded to terrorism or censorship, asks the Open Privacy Research Society.
Still another: “Apple sells iPhones without FaceTime in Saudi Arabia, because local regulation prohibits encrypted phone calls … What happens when local regulations in Saudi Arabia mandate that messages be scanned not for child sexual abuse, but for homosexuality or for offenses against the monarchy?” writes Dr. Nadim Kobeissi.
Scope creep has started: Three weeks ago, tech companies Facebook, Microsoft, Google, and Twitter announced the expansion of an organization tracking violent extremism online called the Global Internet Forum to Counter Terrorism. It’s a very worthy organization too, but the machine-readable data those organizations contribute without external oversight is identical in nature to the techniques Apple is using to scan iPhones.
Learn more: The Apple Privacy Letter project is here.
Fact-checking organization Snopes announced last week that one of its co-founders had plagiarized responses to news articles.
In this era of misinformation and deliberate disinformation, it’s important for you to know that the fact checks themselves remain true. The company says that its investigation has turned up more than fifty instances of executive David Mikkelson using appropriated material from sources like ABC News and The Associated Press.
We told you two months ago about an expose showing that an Amazon warehouse in Scotland was destroying hundreds of thousands of salable items. Amazon UK has launched the Grade and Resell program to resell items that have been returned.
Apple users can now include Android or Windows users on FaceTime calls (although apparently not in Saudi Arabia).
The workaround is web-based. There’s no Android FaceTime app. Instead, an Apple user can send Android and Windows users a link that they can open in a browser.
We’ve written about different brainstorming and creative functions from massive language models like OpenAI’s GPT-3. And we’ve written about how some companies (yes, Google, I mean you) have had trouble balancing the line between in-house ethics professionals and scientists.
OpenAI just released this video of someone typing instructions to a new GPT-3 app that creates code. It’s remarkable and a little scary.
No one will mistake the game that the program writes from natural language as the latest PlayStation hit, but it was done in minutes without sound and including typos. And it was done with someone typing instructions like this: “Animate the rocketship horizontally, bouncing off the left/right walls.”
You’re going to love the rabbit holes you find. Using Wikipedia as a base, a slick interface, and links to video and other media, Histography takes you time traveling.
Check it out here and then set aside some time to go exploring.


It’s August 2nd. The World Wide Web turns 21 years old this week. CERN still maintains the first webpage, called “The Project.“
Today’s Spotlight is 1,229 words — about a 4 1/2 minute read.
Quoted:“After careful consideration of the CDC’s updated guidelines, and in light of current conditions, Twitter has made the decision to close our opened offices in New York and San Francisco as well as pause future office reopenings, effective immediately.” — Twitter statement last Tuesday
a) Google will begin showing verified company logos in Gmail for organizations that authenticate their email server. The company says you’ll start seeing them this year.(9to5Google)
b) Facebook implemented new rules that prohibit advertisers from targeting the interests or activities of 13-17 year old users. Only age, gender, and location can be used to select users to see ads. It’s a significant setback for anyone who sells anything — even entertainment — to middle and high school students. Facebook properties Instagram, Messenger, and WhatsApp are covered by the ban.
c) The Big 5 Tech companies (Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, Facebook, and Microsoft) announced quarterly earnings last week. The five combined in Q2 for $332 billion in revenue and $76.5 billion in net income for the period. That buys a lot of spacecraft. Two areas where the firms seem to have insurmountable leads are cloud computing and advertising. Both experienced double-digit year-over-year growth.
Our take: Facebook in particular enjoyed 56% year-over-year growth in advertising largely due to a 47% increase in ad prices. Since the ads are sold at auction, there are more dollars chasing opportunities, which ultimately increases pricing. We’ve seen that with every Facebook advertising client this quarter. And there’s no pandemic slowdown either. Q2 Facebook ad revenue was up 28% in 2019, 10% in 2020, and 56% this year.
As back-to-school shopping begins in earnest this month, Google is promoting three programs for local retailers. The company says that more than half of school shoppers check online inventory before heading to a store.
Google’s inventory solutions include the ability to run “inventory ads” showing shoppers in search that you have a product in stock. We know that click rates improve when an ad and search result appear on the same page for the same product.
Google also has also introduced a two click product called Pointy for very small retailers. The software is accessible through Google My Business and will connect your Google account and point-of-sale system.
Google also has news for website managers regarding redirects. The company’s Gary Illyes now says that redirects should stay in place for “at least one year,” and advises that they should be kept as long as possible for users. Gary posted this on Twitter and called it a “concrete answer,” which is something they almost never say.
The Justice Department announced last week that the Russian Foreign Intelligence Service had access to emails from 27 US Attorneys offices. Among them were four districts in New York that had at least 80% of their accounts compromised.
What is Solar Winds again? SolarWinds is a software company that was compromised by Russian agents during 2020. Their software then allowed other software to be compromised. Some questions about the company’s finances and cybersecurity practices remain.
Who else was hacked? The U.S. government confirms that agencies within the State, Treasury, Energy, Homeland Security, and Health departments were all hacked. Private companies were also compromised, including Equifax, Cox, Cisco, and Nvidia. The software that was compromised was used by 33,000 organizations.
Details were scant and remain hard to track although we learned this spring that acting Homeland Security director Chad Wolf had his email account compromised.
So they’re still hacking? Last week’s announcement about the US Attorneys hacks was one of the first and most specific with details. There wasn’t a new hack, but we learned more details last week.
What else is new? We’ve talked to more than one technologist about this issue after a friendly organization asked us for a referral. None of the organizations were accepting new business. At the start of this summer, there were 465,000 open cybersecurity jobs in the U.S. Forget plastics. Go into cybersecurity.
Stellar reporting at The Guardian came out last week that alleges a German conspiracy theory group called the Free Citizens of Kassel coordinated anti-lockdown protests in Australia that resulted in more than 60 arrests.
Virtual Private Networks (called VPNs) create a secure connection between you and the internet, but some unscrupulous companies offer free VPN services and then sell your data. Others may be cutting cornersand not using good security practices.
Ars Technica discovered one of those last week from Canadian company Windscribe. Ars’ review found that the company’s servers were left unencrypted among other issues.
Here’s Lifehacker on how to choose a VPN and Wirecutter’s recommendations for two VPN services. The sweet spot for consumer internet retail remains $50-$75 annually so expect to pay in that range for quality VPN services.
Google is doing some security cleanup on files that its users store on Google Drive. If you use that service, you’ve undoubtedly seen security warnings in the last couple of weeks. And you if manage multiple Google networks you’ll have seen many, many security warnings for all the accounts. So. Many. Warnings.
But fear not, because here’s a handy explainer to show you how to accept or remove the new security patch. It’s super-simple and will save you from so many warning messages. Really, just a lot of them.
Let’s preface this whole thing by agreeing that The Next Web’s Tristan Greene is really, really excited about a Google announcement dealing with (squints at paper) a new phase of matter.
OK, so it is a big deal because it could potentially be a tottering step to maybe taking another tottering step. Or watching the soon-to-be walking child fall down on their butt. And that walking has to do with zero-entropy motion. And quantum computers. And really, well, Tristan suggests warp drive and just needs to settle down. But in his defense, he does caveat everything and goes so far as to write, “ … it could accelerate the timeline for quantum computing breakthroughs from “maybe never” to “maybe within a few decades.”
Read about the interesting and cool crystals here.
I’m not going to sell you on using a VPN every week (although you should). But your coffee break today should feature one of my favorite demonstrations: Robin Linus’ excellent tool that shows you on one screen how much information your browser leaks about you.
